构建算法模型(AI算法模型之应用部署概述)
Posted
篇首语:情况是在不断地变化,要使自己的思想适应新的情况,就得学习。本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了构建算法模型(AI算法模型之应用部署概述)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
构建算法模型(AI算法模型之应用部署概述)
模型部署框架类型
算法模型的部署主要可以分成两个方面。一是在移动端/边缘端的部署,即嵌入式,通常以SDK形式呈现。另一个是云端/服务端,通常以服务的形式呈现;今天着重聊聊部署流程,后续移动端部署、具体厂商的智能硬件部署、云端server会开专题介绍。
边缘端
模型训练:通过pytorch、tensorflow等深度学习框架进行训练算法模型,得到模型权重文件,模型训练部分今天不着重介绍,后续专题会展开讨论训练tricks、模型调优、模型剪枝、蒸馏、量化。
模型转化:把权重文件转为对应智能硬件的形态,方便利用对应的GPU、NPU或者IPU智能硬件加速单元来达到加速效果。
算法部署:依照原模型算法推理逻辑对应实现在嵌入式端。
模型转化
包括英伟达、⾼通、华为、AMD在内的⼚家,都在神经⽹络加速⽅⾯投⼊了研发⼒量。通过量化、裁剪和压缩来降低模型尺⼨。更快的推断可以通过在降低精度的前提下使⽤⾼效计算平台⽽达到,其中包括intel MKL-DNN,ARM CMSIS,Qualcomm SNPE,Nvidia TensorRT,海思、RockChip RKNN,SigmarStar SGS_IPU等。
依TensorRT为例,其他平台的部署系列后面会出详细手把手教程。
TensorRT
方式一:把训练得到的权重文件如(pt,pb)先转化为Onnx形式,使用onnx-simplifier对模型进行图优化,得到一个简洁明了的模型图,最后通过trtexec转为对应的engine文件。
以Yolov5为例,导出onnx代码
# YOLOv5 ONNX export try: check_requirements(('onnx',)) import onnx LOGGER.info(f'\\nprefix starting export with onnx onnx.__version__...') f = file.with_suffix('.onnx') torch.onnx.export(model, im, f, verbose=False, opset_version=opset, training=torch.onnx.TrainingMode.TRAINING if train else torch.onnx.TrainingMode.EVAL, do_constant_folding=not train, input_names=['images'], output_names=['output'], dynamic_axes='images': 0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width', # shape(1,3,640,640) 'output': 0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors' # shape(1,25200,85) if dynamic else None) # Checks model_onnx = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model onnx.checker.check_model(model_onnx) # check onnx model # LOGGER.info(onnx.helper.printable_graph(model_onnx.graph)) # print # Simplify if simplify: try: check_requirements(('onnx-simplifier',)) import onnxsim LOGGER.info(f'prefix simplifying with onnx-simplifier onnxsim.__version__...') model_onnx, check = onnxsim.simplify( model_onnx, dynamic_input_shape=dynamic, input_shapes='images': list(im.shape) if dynamic else None) assert check, 'assert check failed' onnx.save(model_onnx, f) except Exception as e: LOGGER.info(f'prefix simplifier failure: e') LOGGER.info(f'prefix export success, saved as f (file_size(f):.1f MB)') return f except Exception as e: LOGGER.info(f'prefix export failure: e')导出后的Onnx模型图
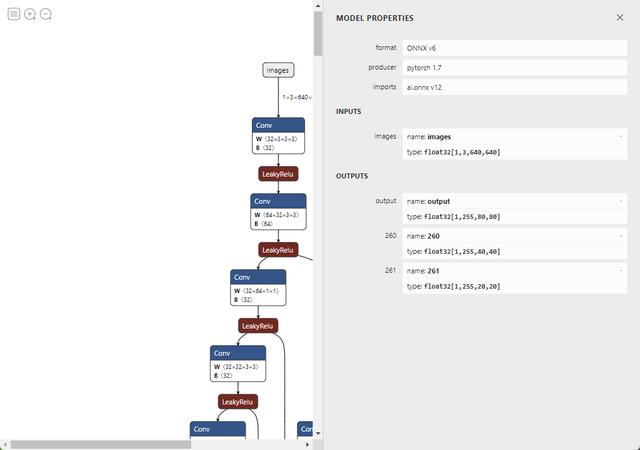
Yolov5-Onnx-结构图
然后执行
trtexec --onnx=weights/yolov5s.onnx --saveEngine=weights/yolov5s.engine对于YOLOV5,官方已经提供了一键转各种格式的脚本,具体参考
在此仅提供模型转化的方法思路。
方式二:根据TensorRT官方API文档,手动搭建模型结构,最后根据API接口把模型转成engine文件。
同样的依照Yolov5为例:
提取模型权重
import sysimport argparseimport osimport structimport torchfrom utils.torch_utils import select_devicedef parse_args(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Convert .pt file to .wts') parser.add_argument('-w', '--weights', required=True, help='Input weights (.pt) file path (required)') parser.add_argument( '-o', '--output', help='Output (.wts) file path (optional)') parser.add_argument( '-t', '--type', type=str, default='detect', choices=['detect', 'cls', 'seg'], help='determines the model is detection/classification') args = parser.parse_args() if not os.path.isfile(args.weights): raise SystemExit('Invalid input file') if not args.output: args.output = os.path.splitext(args.weights)[0] + '.wts' elif os.path.isdir(args.output): args.output = os.path.join( args.output, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(args.weights))[0] + '.wts') return args.weights, args.output, args.typept_file, wts_file, m_type = parse_args()print(f'Generating .wts for m_type model')# Load modelprint(f'Loading pt_file')device = select_device('cpu')model = torch.load(pt_file, map_location=device) # Load FP32 weightsmodel = model['ema' if model.get('ema') else 'model'].float()if m_type in ['detect', 'seg']: # update anchor_grid info anchor_grid = model.model[-1].anchors * model.model[-1].stride[..., None, None] # model.model[-1].anchor_grid = anchor_grid delattr(model.model[-1], 'anchor_grid') # model.model[-1] is detect layer # The parameters are saved in the OrderDict through the "register_buffer" method, and then saved to the weight. model.model[-1].register_buffer("anchor_grid", anchor_grid) model.model[-1].register_buffer("strides", model.model[-1].stride)model.to(device).eval()print(f'Writing into wts_file')with open(wts_file, 'w') as f: f.write('\\n'.format(len(model.state_dict().keys()))) for k, v in model.state_dict().items(): vr = v.reshape(-1).cpu().numpy() f.write(' '.format(k, len(vr))) for vv in vr: f.write(' ') f.write(struct.pack('>f', float(vv)).hex()) f.write('\\n')根据API接口构建编译Yolov5模型结构
核心代码块
ICudaEngine* build_engine(unsigned int maxBatchSize, IBuilder* builder, IBuilderConfig* config, DataType dt, float& gd, float& gw, std::string& wts_name) INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(0U); // Create input tensor of shape 3, INPUT_H, INPUT_W with name INPUT_BLOB_NAME ITensor* data = network->addInput(INPUT_BLOB_NAME, dt, Dims3 3, INPUT_H, INPUT_W ); assert(data); std::map<std::string, Weights> weightMap = loadWeights(wts_name); /* ------ yolov5 backbone------ */ auto conv0 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *data, get_width(64, gw), 6, 2, 1, "model.0"); assert(conv0); auto conv1 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *conv0->getOutput(0), get_width(128, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.1"); auto bottleneck_CSP2 = C3(network, weightMap, *conv1->getOutput(0), get_width(128, gw), get_width(128, gw), get_depth(3, gd), true, 1, 0.5, "model.2"); auto conv3 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_CSP2->getOutput(0), get_width(256, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.3"); auto bottleneck_csp4 = C3(network, weightMap, *conv3->getOutput(0), get_width(256, gw), get_width(256, gw), get_depth(6, gd), true, 1, 0.5, "model.4"); auto conv5 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp4->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.5"); auto bottleneck_csp6 = C3(network, weightMap, *conv5->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), get_width(512, gw), get_depth(9, gd), true, 1, 0.5, "model.6"); auto conv7 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp6->getOutput(0), get_width(1024, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.7"); auto bottleneck_csp8 = C3(network, weightMap, *conv7->getOutput(0), get_width(1024, gw), get_width(1024, gw), get_depth(3, gd), true, 1, 0.5, "model.8"); auto spp9 = SPPF(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp8->getOutput(0), get_width(1024, gw), get_width(1024, gw), 5, "model.9"); /* ------ yolov5 head ------ */ auto conv10 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *spp9->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), 1, 1, 1, "model.10"); auto upsample11 = network->addResize(*conv10->getOutput(0)); assert(upsample11); upsample11->setResizeMode(ResizeMode::kNEAREST); upsample11->setOutputDimensions(bottleneck_csp6->getOutput(0)->getDimensions()); ITensor* inputTensors12[] = upsample11->getOutput(0), bottleneck_csp6->getOutput(0) ; auto cat12 = network->addConcatenation(inputTensors12, 2); auto bottleneck_csp13 = C3(network, weightMap, *cat12->getOutput(0), get_width(1024, gw), get_width(512, gw), get_depth(3, gd), false, 1, 0.5, "model.13"); auto conv14 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp13->getOutput(0), get_width(256, gw), 1, 1, 1, "model.14"); auto upsample15 = network->addResize(*conv14->getOutput(0)); assert(upsample15); upsample15->setResizeMode(ResizeMode::kNEAREST); upsample15->setOutputDimensions(bottleneck_csp4->getOutput(0)->getDimensions()); ITensor* inputTensors16[] = upsample15->getOutput(0), bottleneck_csp4->getOutput(0) ; auto cat16 = network->addConcatenation(inputTensors16, 2); auto bottleneck_csp17 = C3(network, weightMap, *cat16->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), get_width(256, gw), get_depth(3, gd), false, 1, 0.5, "model.17"); /* ------ detect ------ */ IConvolutionLayer* det0 = network->addConvolutionNd(*bottleneck_csp17->getOutput(0), 3 * (Yolo::CLASS_NUM + 5), DimsHW 1, 1 , weightMap["model.24.m.0.weight"], weightMap["model.24.m.0.bias"]); auto conv18 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp17->getOutput(0), get_width(256, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.18"); ITensor* inputTensors19[] = conv18->getOutput(0), conv14->getOutput(0) ; auto cat19 = network->addConcatenation(inputTensors19, 2); auto bottleneck_csp20 = C3(network, weightMap, *cat19->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), get_width(512, gw), get_depth(3, gd), false, 1, 0.5, "model.20"); IConvolutionLayer* det1 = network->addConvolutionNd(*bottleneck_csp20->getOutput(0), 3 * (Yolo::CLASS_NUM + 5), DimsHW 1, 1 , weightMap["model.24.m.1.weight"], weightMap["model.24.m.1.bias"]); auto conv21 = convBlock(network, weightMap, *bottleneck_csp20->getOutput(0), get_width(512, gw), 3, 2, 1, "model.21"); ITensor* inputTensors22[] = conv21->getOutput(0), conv10->getOutput(0) ; auto cat22 = network->addConcatenation(inputTensors22, 2); auto bottleneck_csp23 = C3(network, weightMap, *cat22->getOutput(0), get_width(1024, gw), get_width(1024, gw), get_depth(3, gd), false, 1, 0.5, "model.23"); IConvolutionLayer* det2 = network->addConvolutionNd(*bottleneck_csp23->getOutput(0), 3 * (Yolo::CLASS_NUM + 5), DimsHW 1, 1 , weightMap["model.24.m.2.weight"], weightMap["model.24.m.2.bias"]); auto yolo = addYoLoLayer(network, weightMap, "model.24", std::vector<IConvolutionLayer*>det0, det1, det2); yolo->getOutput(0)->setName(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); network->markOutput(*yolo->getOutput(0)); // Build engine builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(16 * (1 << 20)); // 16MB#if defined(USE_FP16) config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kFP16);#elif defined(USE_INT8) std::cout << "Your platform support int8: " << (builder->platformHasFastInt8() ? "true" : "false") << std::endl; assert(builder->platformHasFastInt8()); config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kINT8); Int8EntropyCalibrator2* calibrator = new Int8EntropyCalibrator2(1, INPUT_W, INPUT_H, "./coco_calib/", "int8calib.table", INPUT_BLOB_NAME); config->setInt8Calibrator(calibrator);#endif std::cout << "Building engine, please wait for a while..." << std::endl; ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config); std::cout << "Build engine successfully!" << std::endl; // Don't need the network any more network->destroy(); // Release host memory for (auto& mem : weightMap) free((void*)(mem.second.values)); return engine;具体参照
方式三:跟方式一一样先转成onnx图模型,根据TensorRT-onnx_parser模型转成engine文件。
核心代码块
bool compile( Mode mode, unsigned int maxBatchSize, const ModelSource& source, const CompileOutput& saveto, std::vector<InputDims> inputsDimsSetup, Int8Process int8process, const std::string& int8ImageDirectory, const std::string& int8EntropyCalibratorFile, const size_t maxWorkspaceSize) if (mode == Mode::INT8 && int8process == nullptr) INFOE("int8process must not nullptr, when in int8 mode."); return false; bool hasEntropyCalibrator = false; vector<uint8_t> entropyCalibratorData; vector<string> entropyCalibratorFiles; if (mode == Mode::INT8) if (!int8EntropyCalibratorFile.empty()) if (iLogger::exists(int8EntropyCalibratorFile)) entropyCalibratorData = iLogger::load_file(int8EntropyCalibratorFile); if (entropyCalibratorData.empty()) INFOE("entropyCalibratorFile is set as: %s, but we read is empty.", int8EntropyCalibratorFile.c_str()); return false; hasEntropyCalibrator = true; if (hasEntropyCalibrator) if (!int8ImageDirectory.empty()) INFOW("imageDirectory is ignore, when entropyCalibratorFile is set"); else if (int8process == nullptr) INFOE("int8process must be set. when Mode is '%s'", mode_string(mode)); return false; entropyCalibratorFiles = iLogger::find_files(int8ImageDirectory, "*.jpg;*.png;*.bmp;*.jpeg;*.tiff"); if (entropyCalibratorFiles.empty()) INFOE("Can not find any images(jpg/png/bmp/jpeg/tiff) from directory: %s", int8ImageDirectory.c_str()); return false; if(entropyCalibratorFiles.size() < maxBatchSize) INFOW("Too few images provided, %d[provided] < %d[max batch size], image copy will be performed", entropyCalibratorFiles.size(), maxBatchSize); int old_size = entropyCalibratorFiles.size(); for(int i = old_size; i < maxBatchSize; ++i) entropyCalibratorFiles.push_back(entropyCalibratorFiles[i % old_size]); else if (hasEntropyCalibrator) INFOW("int8EntropyCalibratorFile is ignore, when Mode is '%s'", mode_string(mode)); INFO("Compile %s %s.", mode_string(mode), source.descript().c_str()); shared_ptr<IBuilder> builder(createInferBuilder(gLogger), destroy_nvidia_pointer<IBuilder>); if (builder == nullptr) INFOE("Can not create builder."); return false; shared_ptr<IBuilderConfig> config(builder->createBuilderConfig(), destroy_nvidia_pointer<IBuilderConfig>); if (mode == Mode::FP16) if (!builder->platformHasFastFp16()) INFOW("Platform not have fast fp16 support"); config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kFP16); else if (mode == Mode::INT8) if (!builder->platformHasFastInt8()) INFOW("Platform not have fast int8 support"); config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kINT8); shared_ptr<INetworkDefinition> network; //shared_ptr<ICaffeParser> caffeParser; shared_ptr<nvonnxparser::IParser> onnxParser; if(source.type() == ModelSourceType::OnnX || source.type() == ModelSourceType::OnnXData) const auto explicitBatch = 1U << static_cast<uint32_t>(nvinfer1::NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH); network = shared_ptr<INetworkDefinition>(builder->createNetworkV2(explicitBatch), destroy_nvidia_pointer<INetworkDefinition>); vector<nvinfer1::Dims> dims_setup(inputsDimsSetup.size()); for(int i = 0; i < inputsDimsSetup.size(); ++i) auto s = inputsDimsSetup[i]; dims_setup[i] = convert_to_trt_dims(s.dims()); dims_setup[i].d[0] = -1; //from onnx is not markOutput onnxParser.reset(nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, gLogger, dims_setup), destroy_nvidia_pointer<nvonnxparser::IParser>); if (onnxParser == nullptr) INFOE("Can not create parser."); return false; if(source.type() == ModelSourceType::OnnX) if (!onnxParser->parseFromFile(source.onnxmodel().c_str(), 1)) INFOE("Can not parse OnnX file: %s", source.onnxmodel().c_str()); return false; else if (!onnxParser->parseFromData(source.onnx_data(), source.onnx_data_size(), 1)) INFOE("Can not parse OnnX file: %s", source.onnxmodel().c_str()); return false; else INFOE("not implementation source type: %d", source.type()); Assert(false); set_layer_hook_reshape(nullptr); auto inputTensor = network->getInput(0); auto inputDims = inputTensor->getDimensions(); shared_ptr<Int8EntropyCalibrator> int8Calibrator; if (mode == Mode::INT8) auto calibratorDims = inputDims; calibratorDims.d[0] = maxBatchSize; if (hasEntropyCalibrator) INFO("Using exist entropy calibrator data[%d bytes]: %s", entropyCalibratorData.size(), int8EntropyCalibratorFile.c_str()); int8Calibrator.reset(new Int8EntropyCalibrator( entropyCalibratorData, calibratorDims, int8process )); else INFO("Using image list[%d files]: %s", entropyCalibratorFiles.size(), int8ImageDirectory.c_str()); int8Calibrator.reset(new Int8EntropyCalibrator( entropyCalibratorFiles, calibratorDims, int8process )); config->setInt8Calibrator(int8Calibrator.get()); INFO("Input shape is %s", join_dims(vector<int>(inputDims.d, inputDims.d + inputDims.nbDims)).c_str()); INFO("Set max batch size = %d", maxBatchSize); INFO("Set max workspace size = %.2f MB", maxWorkspaceSize / 1024.0f / 1024.0f); INFO("Base device: %s", CUDATools::device_description().c_str()); int net_num_input = network->getNbInputs(); INFO("Network has %d inputs:", net_num_input); vector<string> input_names(net_num_input); for(int i = 0; i < net_num_input; ++i) auto tensor = network->getInput(i); auto dims = tensor->getDimensions(); auto dims_str = join_dims(vector<int>(dims.d, dims.d+dims.nbDims)); INFO(" %d.[%s] shape is %s", i, tensor->getName(), dims_str.c_str()); input_names[i] = tensor->getName(); int net_num_output = network->getNbOutputs(); INFO("Network has %d outputs:", net_num_output); for(int i = 0; i < net_num_output; ++i) auto tensor = network->getOutput(i); auto dims = tensor->getDimensions(); auto dims_str = join_dims(vector<int>(dims.d, dims.d+dims.nbDims)); INFO(" %d.[%s] shape is %s", i, tensor->getName(), dims_str.c_str()); int net_num_layers = network->getNbLayers(); INFO("Network has %d layers:", net_num_layers); for(int i = 0; i < net_num_layers; ++i) auto layer = network->getLayer(i); auto name = layer->getName(); auto type_str = layer_type_name(layer); auto input0 = layer->getInput(0); if(input0 == nullptr) continue; auto output0 = layer->getOutput(0); auto input_dims = input0->getDimensions(); auto output_dims = output0->getDimensions(); bool has_input = layer_has_input_tensor(layer); bool has_output = layer_has_output_tensor(layer); auto descript = layer_descript(layer); type_str = iLogger::align_blank(type_str, 18); auto input_dims_str = iLogger::align_blank(dims_str(input_dims), 18); auto output_dims_str = iLogger::align_blank(dims_str(output_dims), 18); auto number_str = iLogger::align_blank(format("%d.", i), 4); const char* token = " "; if(has_input) token = " >>> "; else if(has_output) token = " *** "; INFOV("%s%s%s %s-> %s%s", token, number_str.c_str(), type_str.c_str(), input_dims_str.c_str(), output_dims_str.c_str(), descript.c_str() ); builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize); config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(maxWorkspaceSize); auto profile = builder->createOptimizationProfile(); for(int i = 0; i < net_num_input; ++i) auto input = network->getInput(i); auto input_dims = input->getDimensions(); input_dims.d[0] = 1; profile->setDimensions(input->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kMIN, input_dims); profile->setDimensions(input->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kOPT, input_dims); input_dims.d[0] = maxBatchSize; profile->setDimensions(input->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kMAX, input_dims); // not need // for(int i = 0; i < net_num_output; ++i) // auto output = network->getOutput(i); // auto output_dims = output->getDimensions(); // output_dims.d[0] = 1; // profile->setDimensions(output->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kMIN, output_dims); // profile->setDimensions(output->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kOPT, output_dims); // output_dims.d[0] = maxBatchSize; // profile->setDimensions(output->getName(), nvinfer1::OptProfileSelector::kMAX, output_dims); // config->addOptimizationProfile(profile); // error on jetson // auto timing_cache = shared_ptr<nvinfer1::ITimingCache>(config->createTimingCache(nullptr, 0), [](nvinfer1::ITimingCache* ptr)ptr->reset();); // config->setTimingCache(*timing_cache, false); // config->setFlag(BuilderFlag::kGPU_FALLBACK); // config->setDefaultDeviceType(DeviceType::kDLA); // config->setDLACore(0); INFO("Building engine..."); auto time_start = iLogger::timestamp_now(); shared_ptr<ICudaEngine> engine(builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config), destroy_nvidia_pointer<ICudaEngine>); if (engine == nullptr) INFOE("engine is nullptr"); return false; if (mode == Mode::INT8) if (!hasEntropyCalibrator) if (!int8EntropyCalibratorFile.empty()) INFO("Save calibrator to: %s", int8EntropyCalibratorFile.c_str()); iLogger::save_file(int8EntropyCalibratorFile, int8Calibrator->getEntropyCalibratorData()); else INFO("No set entropyCalibratorFile, and entropyCalibrator will not save."); INFO("Build done %lld ms !", iLogger::timestamp_now() - time_start); // serialize the engine, then close everything down shared_ptr<IHostMemory> seridata(engine->serialize(), destroy_nvidia_pointer<IHostMemory>); if(saveto.type() == CompileOutputType::File) return iLogger::save_file(saveto.file(), seridata->data(), seridata->size()); else ((CompileOutput&)saveto).set_data(vector<uint8_t>((uint8_t*)seridata->data(), (uint8_t*)seridata->data()+seridata->size())); return true; ; //namespace TRTBuilder具体参照
至此模型转化这部分完成。
三种方式的优缺点:
方式一、方式三相对于方式二更为简单方便快捷,特别方式一零代码即可实现模型的转化,反观方式二需要清晰模型结构,清晰API接口算子并手撸代码完成构建engine。但方式一、方式三对于一些模型如transform、Vit模型由于一些算子还未支持,故不能一键转化,而方式二则可完成,总体来说方式二相比其他更为灵活,但上手难度更大。
算法部署
整体流程

流程图
输入:着重说下视频流如rtsp、webrtc、rtmp这种实时视频流,我们需要先对流进行解码从而得到RGB图像(YUV420、NV12、NV21 -> RGB),其中解码又分为软解码和硬解码,软解码如libx264,libx265等,硬解码如Nvidia的CUVID以及海思,RockChip的Mpp等,关于视频流的编解码后续会开专题详细介绍。
预处理:把得到的RGB图像依照跟训练时进行同样的预处理,如Yolov5需要自适应缩放、归一化操作;人脸检测scrfd需要自适应缩放、减均值127.5,除方差128等操作;对于自适应缩放可以采用仿射变换、letterbox的形式实现;对于减均值、除方差,NVIDIA可以采用CUDA进行操作,从而达到提速的效果。
模型推理:把经过上边两步的图像data送进序列化好的engine进行model_forward,得到output_tensor。
后处理:把上述得到的output_tensor,进行后处理decode,依照目标检测为例这个操作一般为general_anchor、nms、iou,坐标映射到原图(transform_pred)等操作;分类模型则一般为get_max_pred;姿态识别模型一般为keypoints_from_heatmap、transform_pred等。
输出:经过后处理后,就得到了最终的输出结果,如检测项,分类类别,keypoints,人脸坐标等等,最终可根据实际场景进行告警推送等应用开发,或者把告警图片进行编码(RGB->YUV420)以视频流的方式推送到流媒体服务器。
生成SDK
对于Hisi3516、3519或者rv1126、rv1109这类平台,flash空间小,需要交叉编译,可打包成动态链接库,提供接口函数供上层应用调用;对于rv3399、rk3568、jetson产品自带Ubuntu或者Linaro系统,可终端机自行编译,并且可部署python,可利用pybind11进行衔接交互。
云服务端
关于模型的云端部署,业界也有许多开源的解决方案,但目前为止来看,还没有一种真的可以一统业界,或者说称得上是绝对主流的方案。
针对云端部署的框架里,我们可以大致分为两类,一种是主要着力于解决推理性能,提高推理速度的框架,这一类里有诸如tensorflow的tensorflow serving、NVIDIA基于他们tensorRt的Triton(原TensorRt Serving),onnx-runtime,国内的paddle servering等, 将模型转化为某一特定形式(转化的过程中可能伴有一些优化的操作), 并对外提供服务,以此来获得相对较高的性能。
另一类框架主要着眼于结合模型整个生命周期,对模型部署进行管理,比如mlflow、seldon、bentoml、cortex等等,这些框架的设计与思路其实五花八门,有的为了和训练部分接轨,把模型文件管理也纳入了。有的则是只管到容器编排的部分,用户需要自己做好容器,它帮你发到k8s上之类的(这种情况甚至能和第一类框架连起来用)。当然也有专注于模型推理这一小块的。
写在最后
算法应用落地部署已然成为AI领域关键的一环,由于国外产品制裁,我们也大力支持国产智能硬件AI落地,已在海思、瑞芯微、sigmastar、寒武纪、地平线等国产芯片部署多款算法,如目标检测(YOLOV5等)、人脸识别(scrfd+arcface等)、姿势识别(lite-hrnet等)、动作序列识别(tsm等),目标追踪(MOT,bytetrack),拥有多行业、多领域真实数据集,并形成多款AI智能产品,落地应用在安防、加油站、充电桩、火车站、商场等各大行业,后续也会开设专题介绍各大智能硬件、各大算法的详细部署流程,致力于发展壮大国产AI部署社区生态。
今天就先到这里,谢谢,点点关注不迷路。

相关参考